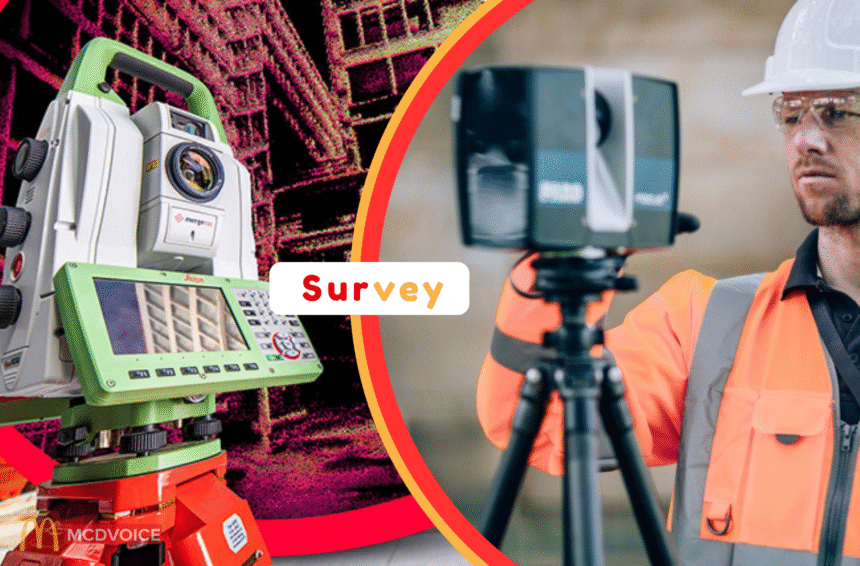
The world of surveying has undergone a remarkable transformation with the introduction of 3D laser scanning survey technology. This innovative tool has revolutionized how we collect, measure, and analyze spatial data, offering unparalleled accuracy, speed, and detail. If you’re unfamiliar with 3D laser scanning or are curious about its benefits, this guide will provide you with all the essential information you need to understand this powerful surveying technology.
Quick Bio Table
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Technology | 3D Laser Scanning Survey Technology |
| Primary Use | Data collection, mapping, and modeling |
| Key Benefit | High accuracy and speed |
| Point Cloud | Digital representation of scanned data |
| Precision | Millimeter-level accuracy |
| Industries Served | Construction, architecture, civil engineering, manufacturing |
| Speed | Rapid data collection in hours, as opposed to days |
| Non-Contact | Safe, non-invasive data collection |
| Applications | Building scans, heritage conservation, terrain mapping |
| Integration | Works with CAD and BIM software for further analysis |
| Data Format | Point clouds, 3D models |
What is 3D Laser Scanning Survey?
At its core, 3D laser scanning is a method of capturing precise measurements of physical environments or objects. Using laser beams, a 3D laser scanner emits thousands—or even millions—of laser points to map the surface of a structure. This process creates a digital representation known as a point cloud, which is a detailed 3D model of the scanned area.
Unlike traditional surveying methods that rely on measuring instruments, 3D laser scanning captures vast amounts of data in seconds, making it significantly faster and more accurate. The technology is especially useful in complex environments where conventional methods fall short, such as in construction, engineering, and heritage preservation.
How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
The working principle behind 3D laser scanning is relatively simple but highly effective. The scanner emits laser pulses that bounce back after hitting an object or surface. The scanner then records the time it takes for the laser to return, using this data to calculate the exact distance to the surface. The process is repeated millions of times per second to gather data from every angle of the scanned area.
This data is then processed into a point cloud, a collection of points in 3D space that represent the scanned environment. From the point cloud, surveyors can generate highly detailed 3D models, which can be imported into various CAD (computer-aided design) and BIM (building information modeling) software tools for further analysis and planning.
Key Advantages of 3D Laser Scanning

Accuracy and Precision
One of the most significant advantages of 3D laser scanning is its precision. Unlike traditional methods that can be prone to human error, laser scanning can capture measurements with millimeter-level accuracy. This makes it ideal for complex projects where every detail matters.
Speed
A typical 3D laser scan can cover an entire building or site in a fraction of the time it would take a surveyor to gather the same data using manual methods. This rapid data collection is invaluable, particularly in large-scale projects such as construction or urban planning.
Non-Invasive
3D laser scanning is a non-contact method of data collection. This means surveyors can capture data from a distance without physically interacting with the object or environment. This makes the technology ideal for surveying in hazardous or hard-to-reach areas, such as during structural assessments or archaeological excavations.
Data Richness
Unlike traditional methods, which often rely on a limited number of measurements, 3D laser scanning generates millions of data points. This extensive data set allows for a far richer and more detailed representation of the environment, which can be crucial for design, analysis, and decision-making.
Real-Time Feedback
With modern 3D laser scanning tools, surveyors can view the scanned data in real-time, providing instant feedback on the quality and coverage of the scan. This allows them to make adjustments immediately, ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the survey.
Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Survey Technology
Architecture and Construction
In architecture and construction, 3D laser scanning is used to create as-built models of structures. These models serve as the basis for renovations, extensions, and other construction projects. Laser scanning allows for precise documentation of existing conditions, ensuring that designs align with the current state of the building.
Heritage Preservation
3D laser scanning has become an essential tool in preserving historical buildings and artifacts. By creating detailed 3D models, it’s possible to digitally store the exact measurements and features of historical sites, helping to safeguard them for future generations.
Engineering and Manufacturing
Engineers and manufacturers use 3D laser scanning to reverse engineer parts, conduct quality control, and ensure products meet specifications. This technology allows for quick and accurate inspections, which can reduce defects and improve manufacturing processes.
Civil Engineering and Infrastructure
For civil engineers, 3D laser scanning is invaluable in mapping terrain, assessing infrastructure, and planning large-scale projects like highways, bridges, and tunnels. The data collected can be used to create digital elevation models (DEMs) that help in the planning and design stages.
Mining and Excavation
In the mining industry, 3D laser scanning helps map mines and tunnels, providing precise information on their structure and condition. This information is essential for maintaining safety standards and optimizing excavation processes.
The Future of 3D Laser Scanning Technology

As technology continues to evolve, 3D laser scanning will only become more powerful and accessible. The rise of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, which uses laser pulses to measure distances, is expanding the applications of laser scanning, particularly in autonomous vehicles and aerial mapping using drones.
Additionally, advancements in cloud computing are enabling the storage and processing of massive datasets collected by laser scanners. This means that large-scale surveys can be conducted remotely, and the resulting models can be accessed and analyzed in real-time from anywhere in the world.
Why You Should Consider Using 3D Laser Scanning
For any surveying professional or project manager, adopting 3D laser scanning can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of data collection. Whether you’re involved in architecture, construction, engineering, or heritage conservation, the benefits of using this technology are clear.
Free Offers, Survey, and Rewards!
To encourage the use of 3D laser scanning technology, many companies now offer free trials, discounts, and gift cards to customers who book their services. These offers can help reduce the cost of your first project and give you a hands-on experience with the technology before committing fully. Additionally, many firms reward loyal customers with coupons and feedback incentives, offering significant savings on future surveys or technology upgrades.
How to Get Started with 3D Laser Scanning Survey Technology
Choosing the Right Service Provider
If you’re considering 3D laser scanning for your project, it’s crucial to choose a reputable service provider who can guide you through the process. Look for a company that offers high-quality equipment, experienced surveyors, and detailed data analysis.
Understanding Your Project Needs
Before starting your 3D laser scanning survey, it’s important to clearly define your project’s needs. Are you looking to scan a building, a piece of machinery, or a large landscape? Understanding your specific requirements will help you choose the right scanning tools and methods.
Review the Costs and Benefits
While 3D laser scanning technology can be an investment, the benefits it offers in terms of accuracy, speed, and data richness far outweigh the initial costs. Most projects will find that the long-term savings in time and labor make it a highly cost-effective option.
People Read Also: The Power of 360 Surveys for Managers: Gaining Insight and Driving Growth
Conclusion
3D laser scanning technology is an exciting and innovative advancement in the field of surveying. Its ability to provide accurate, detailed, and fast data makes it an invaluable tool across various industries, from architecture to civil engineering. As the technology continues to evolve, it will only become more integrated into everyday surveying practices, offering greater efficiency, accuracy, and possibilities for future projects. Whether you’re a professional surveyor or someone new to the field, understanding the power of 3D laser scanning is the first step toward leveraging its many benefits for your projects.
(FAQs)
What is 3D laser scanning survey technology?
3D laser scanning survey technology uses laser beams to capture detailed measurements of objects or environments. The technology generates a point cloud, a digital 3D model, from these measurements, allowing for precise data collection and analysis.
What industries benefit from 3D laser scanning?
Industries like construction, architecture, engineering, heritage preservation, civil engineering, and manufacturing all benefit from 3D laser scanning technology due to its speed, accuracy, and ability to gather detailed data in complex environments.
How accurate is 3D laser scanning?
3D laser scanning provides millimeter-level accuracy, making it significantly more precise than traditional measurement techniques. This accuracy ensures that measurements are reliable, even in intricate and hard-to-reach areas.
How long does a 3D laser scan take?
The time required for a 3D laser scan depends on the size and complexity of the area being scanned. However, the process is significantly faster than traditional methods, with large areas scanned in just a few hours.
Is 3D laser scanning cost-effective?
While the initial investment in 3D laser scanning equipment may be higher, it offers significant long-term savings by reducing labor costs, improving accuracy, and speeding up the data collection process. For many projects, the benefits outweigh the initial cost.